Need help? We're here to assist you!
Thank You for Enquiry, we will contact you soon!
Close
The Class 7 is an important year in a student’s life and Science is one of the subjects that require dedication, hard work, and practice. It’s a subject where you can score well if you are well-versed with the concepts, remember the important formulas and solving methods, and have done an ample amount of practice. Worry not! Home Revise is here to make your Class 7 journey even easier. It’s essential for students to have the right study material and notes to prepare for their board examinations, and through Home Revise, you can cover all the fundamental topics in the subject and the complete NCERT Class 7 Science Book syllabus.

Exercise Questions
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called_____________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called_____________.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as _____________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as _____________.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of _____________, _____________ and _____________.
Solution:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called vegetative propagation
.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual flower
.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as Pollination
.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as fertilisation
.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind
, water
and animals
.
2. Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Solution:
Different methods of asexual reproduction are as follows:
Vegetative Propagation
In this asexual reproduction, new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds of the individual plant.
Examples – Tuber of potato, the rhizome of ginger.
Budding
The bud is a small projection which gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell. The new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells.
Example – Yeast.
Fragmentation
In this mode of reproduction, the growth and multiplication are done by rapidly breaking down into two or more fragments. Each fragment grows into new individuals when water and nutrients are available.
Example – Algae
Spore Formation
This reproduction is done by spores which, under favourable conditions, germinate and develop into a new individual.
Examples – Fungi like Rhizopus, Mucor, etc.
Fission
It is a type of asexual reproduction where the unicellular organism splits to form new organisms. There are two types of fission which are,
Examples
Unicellular organisms that undergo binary fission are amoeba, paramecium, leishmania, etc.
Plasmodium undergoes the process of multiple fission.
3. Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Solution:
Sexual reproduction is a method where male and female gametes fuse to form a new individual. In plants, stamens and pistils are male and female reproductive organs which bear the anthers and ovary, respectively.
4. State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Solution:
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| It requires only one parent | Requires a male and female parent |
| Daughter cells formed are identical to parents and to each other. | Newly formed offsprings show variations in comparison to the parents. |
| Special reproductive organs are not required | Special reproductive organs are required |
| Ex: Yeast, rose, jasmine | Ex: Insects, animals |
5. Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Solution:
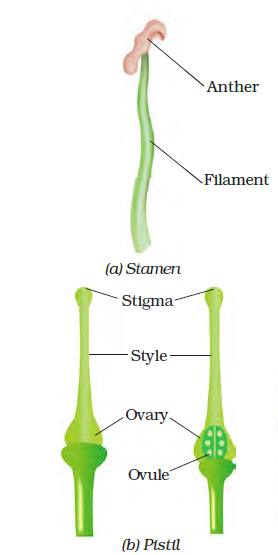
6. Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Solution:
| Self-pollination | Cross-pollination |
| In self-pollination, pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower. | In cross-pollination, pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same kind. |
| Self-pollination occurs only in bisexual flowers | It occurs in both unisexual and bisexual flowers |
7. How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Solution:
The process of fusion of male and female gametes (to form a zygote) is called fertilisation. The zygote develops into an embryo, and the embryo undergoes mitotic cell division to form seeds.
8. Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Solution:
Seeds and fruits of plants are carried away by the wind, water and animals. Winged seeds such as those of drumstick and maple, light seeds of grasses or hairy seeds of aak (Madar) and hairy fruit of the sunflower get blown off with the wind to faraway places. Some seeds are dispersed by water. These fruits or seeds usually develop floating ability in the form of a spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut. Some seeds are dispersed by animals, especially spiny seeds with hooks which get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places. Examples are Xanthium and Urena. Some seeds are dispersed when the fruits burst with sudden jerks. The seeds are scattered far from the parent plant. This happens in the case of castor and balsam.
9. Match items in Column I with those in Column II: Column I Column II
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (a) Bud | (i) Maple |
| (b) Eyes | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (c) Fragmentation | (iii) Yeast |
| (d) Wings | (iv) Bread mould |
| (e) Spores | (v) Potato |
| (vi) Rose |
Solution:
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (a) Bud | (iii) Yeast |
| (b) Eyes | (v) Potato |
| (c) Fragmentation | (ii) Spirogyra |
| (d) Wings | (i) Maple |
| (e) Spores | (iv) Bread mould |
10. Tick the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf (ii) stem (iii) root (iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation (ii) pollination (iii) reproduction (iv) seed formation
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed (ii) stamen (iii) pistil (iv) fruit
(d) A spore-producing organism is
(i) rose (ii) bread mould (iii) potato (iv) ginger
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem (ii) leaves (iii) roots (iv) flower
Solution:
a) (iv) flower
b) (i) fertilization
c) (iv) fruit
d) (ii) bread mould
e) (ii) leaves
The 12th chapter is quite important, so we have tailored perfect study materials for students to understand the concepts of plant reproduction and score well in the examination. These notes cover the most important topics like types of reproduction, how plants reproduce, seed formation, seed dispersal, etc.
The production of new offspring from parents is known as reproduction. Reproduction in plants is a new concept for students of 7th standard. This chapter introduces the mode of reproduction in plants. Going further, this topic sheds knowledge on sexual reproduction, fruits and seed formation and seed dispersal.
In addition to these solutions, BYJU’S offers top subject experts with relevant experience to guide students and help them learn the subject in a more engaging, easy, detailed and clear manner. Students are also provided with regular feedback on their performance. We also have a responsive support team, and students can approach them to clear all their doubts. Meanwhile, students can also have a glimpse of BYJU’S – The Learning App for a more efficient as well as fun learning experience.